In the following tutorial we will present way how to perform a SCAP based security scan of RHEL 7 Docker containers and images.
This tutorial will also describe some basic usage of Docker. If you have running RHEL 7 Docker container, you can skip these sections and go directly to Install oscap-docker section.
1. What is Docker?
As official website docker.com says, “Docker is an open platform for building, shipping and running distributed applications”.
Sentence from previous probably doesn’t help you to understand what the Docker is, so I will use some abstraction/simplification to describe it.
Docker is chroot on steroids. It allows you to create a container containing some Linux-based distribution. This container can contains your application and preinstalled dependencies applied settings required by your application. So you can deploy this package as Docker image to your customer.
2. Getting Docker
To get an environment where you can run Docker containers, you can install Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 (RHEL 7) as a container host. To make docker package available via yum, you have to add RHEL Extras repository. Here step-by-step guide how to install Docker on your RHEL7 host:
- Install RHEL 7 Server edition
- Register RHEL using subscription-manager tool
- Enable extras repositories
# subscription-manager repos --enable=rhel-7-server-extras-rpms # subscription-manager repos --enable=rhel-7-server-optional-rpms
- Install Docker
# yum install docker docker-registry # yum install device-mapper-libs device-mapper-event-libs
- Enable and start docker service
# systemctl enable docker.service # systemctl start docker.service
-
Check Docker status
# systemctl status docker.service
Docker can be controlled by docker command-line tool
3. Using Docker
This section should helps you with creation of a RHEL 7 based container which we want to scan.
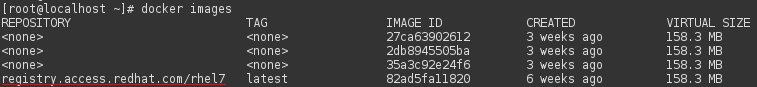
3.1 Get RHEL 7 Docker image
3.2 Run RHEL7 container
We have downloaded required image in previous paragraph, now we want to run container from the image.
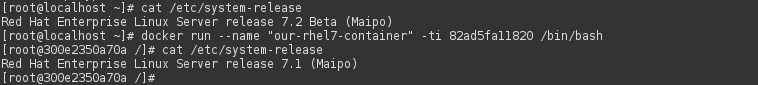
# docker run --name "our-rhel7-container" -ti registry.access.redhat.com/rhel7 /bin/bash
This command will start new container called “our-rhel7-container” and gives us interactive interface. We can see, that we have connected from RHEL 7.2 beta host to container with RHEL 7.1. Now, we can exit container by typing exit to shell of the container. You can get list running containers by
# docker ps
or list of all containers(running and not running) by
# docker ps -a
4. Install oscap-docker
OpenSCAP tools are separated into several packages. We will use the oscap-docker tool from package openscap-containers. You can install it by:
# yum install openscap-containers
Also, make sure that you have installed the Atomic backend and other related packages:
# yum install atomic docker python-docker-py
The oscap-docker is a simple tool providing interface to use oscap in Docker environment. It allows you to scan running Docker containers and images almost in the same way as scan of local machine.
5. Scan Docker containers and images
At this phase, we have installed all required tools and prepared environment for perform security scan.
We need to have running container, but fortunately we can use container from previous sections. To start this container again, we can use this command:
# docker start our-rhel7-container
The usage of oscap-docker is quite simple, command has usually this format:
# oscap-docker <image/container>[-cve] <image/container identifier> <oscap parameters>
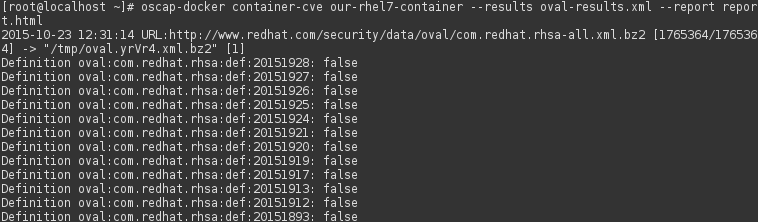
5.1 CVE scan of container
5.2 Scan Docker container using custom security policy
There is an option to use your custom security-policy to scan container. We would use SSG in this example. At first, we have to install it. It install SSG SCAP security content to “/usr/share/xml/scap/ssg/content/”.
# yum install scap-security-guide
Now, we perform scan using custom content.
# oscap-docker container our-rhel7-container xccdf eval \
--profile ospp --report report.html \
/usr/share/xml/scap/ssg/content/ssg-rhel7-ds.xml
5.3 Scanning of images
You can also scan Docker images in the same way. In the following example, we will scan against a profile of our choice.
# oscap-docker image registry.access.redhat.com/rhel7 xccdf eval \
--profile ospp --report report.html \
/usr/share/xml/scap/ssg/content/ssg-rhel7-ds.xml
6. Further resources
You can get more info about oscap-docker using oscap-docker -h or man oscap-docker.
These sections from the Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 Documentation cover container scanning: